Posts Tagged ‘Sporadic-E’
 LHS Episode #193: All About AREDN
LHS Episode #193: All About AREDN
 This is the 193rd episode of Linux in the Ham Shack. In this episode, your hosts discuss ARRL Field Day, JT65 and new modes like it, the wonder of 6m and the E Layer, the NSA, patent trolls, useful command line utilities and more. We also have a great interview with Joe Ayers, AE6XE, about AREDN, the Amateur Radio Emergency Data Network. This one runs a bit long, but we thought it was worth it.
This is the 193rd episode of Linux in the Ham Shack. In this episode, your hosts discuss ARRL Field Day, JT65 and new modes like it, the wonder of 6m and the E Layer, the NSA, patent trolls, useful command line utilities and more. We also have a great interview with Joe Ayers, AE6XE, about AREDN, the Amateur Radio Emergency Data Network. This one runs a bit long, but we thought it was worth it.
73 de The LHS Crew
 JT65 Bringing New Activity To 50MHz
JT65 Bringing New Activity To 50MHz
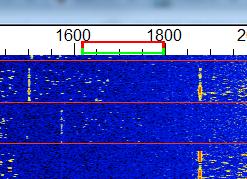 |
| JT65 Waterfall |
As mentioned in previous blogs, this summer's Es season on 50MHz has seen a huge increase in the number of stations using the weak-signal JT65 mode.
Although this mode has been around for a few years, for some reason, it really took off this season. I witnessed many long-time, 'CW-forever' operators (myself included), gingerly move up the band to see what this mode could offer.
At first I thought the activity I was seeing was probably mostly from magic-band regulars, who like me, were also curious ... but I now think this is not the case.
Normally, my 6m summertime Es activities result in just one or two stations requesting a QSL to confirm the contact. These are usually guys that either need a VE7 card or are looking to confirm my grid-square ... just a few cards arrive, in spite of many dozens of contacts over the summer months. This summer I noticed a much different pattern.
This summer saw a tenfold increase in the number of QSL requests and every single one was for a JT65 or JT9 digital mode contact! It soon became apparent that these were not 6m diehards that had just moved up the band, but rather, very enthusiastic newcomers to the band ... what an exciting thing to see! Many of the cards did not have any grid-square information ... the telltale sign of all VHF operators. They had discovered the magicband, using JT65.
Perhaps these were mostly 'no-code' amateurs or those living in antenna-challenged situations such as condos or apartments. Whatever the reason, it really is interesting to see such a profound change in 6m operating tactics, by both the veteran ops and by the newcomers ... all happening so quickly. Hopefully some of the new arrivals will venture down the band to try CW or SSB where contacts can be made much more quickly than on the digital modes but all of this new activity is wonderful to see.
 6m Es – Is It Changing?
6m Es – Is It Changing?
With the summer Sporadic-E season now approaching its midpoint, it looks as though this year may be another poor one. Having been operating on 6m every summer since the early 70's, I'm beginning to believe that we may be seeing some changes in what was once the normal summer pattern.
This summer, I can count on one hand, the number of good solid openings ... openings lasting for several hours. Over the past forty plus years, summers on 'six' for me, here in southwestern BC, were usually very predictable. The last week of May would usually see the start of regular band openings that would quickly escalate to almost daily openings through June and July. It was not uncommon to see the band open all day, into the very late hours and then still be open the next morning. Intense Es from California predominated the 70's and 80's ... much different than the past several summers here. The stronger openings now, when they occur, seem to be more to the southeast, favoring Colorado and other nearby central states. At times, this will turn into double-hop to the southeastern states, usually favoring the 'EM' grids.
Really long-haul openings have also taken on a different flavor. For more than two decades, openings to Japan on Sporadic-E almost always occurred late at night, near midnight ... late afternoon for the JAs'. The openings rarely favored anything other than the west coast. Openings to Europe from the west coast were, for the most part unheard of, and any claims of summer-time EU contacts were often dismissed as 'wishful thinking' and not taken too seriously.
A huge shift in long haul Es over the past decade has pretty much re-written the rules of what we have always taken to be 'normal'. Summertime openings to Europe, from the west coast, have now become a regular expectance and, although still rare and usually short-lived, somewhat dependable. Our midnight openings to Japan have largely disappeared ... replaced by hour-long, mid-afternoon or dinner-hour JA runs, and more often than not, right over our west coast heads to any U.S. call district fortunate enough to be in the propagation's hot-spot. All of this is so very different than the 70's and 80's!
So why are things different now? Is it subtle influences from our ever-changing sun?

We are now heading into our sixth straight day of a spotless sun, but in reality, solar activity has been slowly winding down for the last several years. Long term studies tend to show that the solar cycle has little effect on summertime Es, but maybe not.
Is it climatic change ... global-warming? The e-layer is supposedly high above any weather influence yet there is evidence pointing to Es being associated with lightning storms and high altitude plasma-driven sprite activity. Maybe global-warming includes ionospheric changes as well and perhaps weather plays more of a role than previously thought.
 |
| Courtesy: http://www.astrosurf.com/luxorion/qsl-perturbation.htm |
Is it changes in equipment, with an ever-increasing number of 6m stations sporting huge antenna systems and higher ERPs' than ever before?
| Six 7-el Stacked Yagis At W7EW |
Maybe it's the influence of the Internet on operating practices? There is no doubt that having the ability to watch and follow realtime propagation paths, by the very minute, has made a huge difference in operating strategies ... along with big payoffs when it comes to catching those fleeting openings that would likely otherwise have gone unnoticed. On more than one occasion, I have worked Europeans on a seemingly 'dead band', with no propagation indicators at all ... just an announcement on the Internet that said station was calling 'CQ' at the time. Perhaps nowadays, there are just more savvy operators with good stations and a much better understanding of the DX possibilities ... slowly wringing out the best of what 6m has to offer. Maybe it's a combination of several factors.
Let me qualify my observations by saying that these have been my experiences and perhaps unique to the PNW and southwest VE7 only. Longtime Es data-collector, WA5IYX (Pat) in Texas, graphically shows the yearly Es variance in his region. The pattern appears somewhat sinusoidal in nature over the past few decades, but except for the occasional 'stinker', the variances from one summer to the next are not huge.
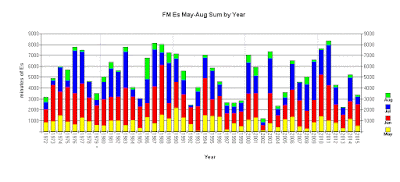 |
| Annual Es At WA5IYX courtesy: http://www.qsl.net/wa5iyx/ |
Are my observations similar to what you may have observed over the past many years? Are the changes real or only imagined? As with most global events being driven by mother nature and continually dynamic, I see no reason why 6m propagation should remain constant from decade to decade ... but I'd sure like to see a little more of it.
Now, usually when I voice complaints about our bad 6m propagation, it seems that things often flip from terrible to amazing soon after. The best Es of the summer often peaks in or close to the first week of July, now fast approaching. Let's hope that this is one 'constant' that hasn't changed as well!
**********************************
Wouldn't you know it. I put above blog together on Tuesday evening, intending to publish it on Wednesday. Early Wednesday morning, before 0900 local time, several Europeans were worked on CW ... perhaps the propagation gods were looking over my shoulder?
As is so often the case with these relatively new types of openings between EU and the west coast, there were no particular propagation clues from this end, other than a brief reception of the KØGUV/b in Minnesota. I was only alerted by the EU propagation reaching as far west as Colorado (KØGU) and a posting on the ON4KST 6m propagation logger that K7RWT in Oregon was hearing the VA5MG/b, sometimes a precursor to PNW propagation over the pole. The propagation map at the time shows no real indicators out this way ... once again, the value of realtime prop-watching via the Internet seems to have played a big role in finding these types of openings.
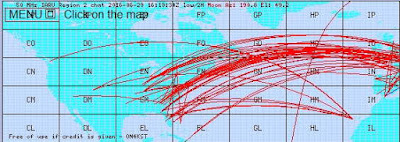 |
| courtesy: http://www.on4kst.org/ |
 6m Awakens
6m Awakens
 Well Friday morning's planned 2m EME window got pushed to the side when 6m started to show some interesting propagation possibilities. Several Europeans had been working slowly westward, past their usual east coast stopping point. When EA8DBM (Alex) in the Canary Islands reported via the ON4KST 6m chat page that he was hearing a station in Montana, my ears really perked up. At around 10:30 local time, KE7V (Johnny), about 40 miles due south of me in Washington state, was heard working Alex but I could hear nothing from him at all.
Well Friday morning's planned 2m EME window got pushed to the side when 6m started to show some interesting propagation possibilities. Several Europeans had been working slowly westward, past their usual east coast stopping point. When EA8DBM (Alex) in the Canary Islands reported via the ON4KST 6m chat page that he was hearing a station in Montana, my ears really perked up. At around 10:30 local time, KE7V (Johnny), about 40 miles due south of me in Washington state, was heard working Alex but I could hear nothing from him at all. As is often the case between here and KE7V, signals from Europe often move quickly northward and sure enough, about two minutes later, EA8DBM's CW signal appeared at good strength, calling CQ.
I quickly worked Alex, whose signal stayed around for almost an hour, and then began looking for any others that might be riding along on the same path. Sure enough, his neighbour, EA8TL was heard CQ'ing, but much weaker. After a few calls he came back with my report to which I responded several times, but it was evident that he was having difficulty as he kept repeating my report. Unfortunately, and unlike Alex, he soon faded away without me ever hearing the needed 'RR' for my signal report confirmation.
About an hour later, a rapidly fading and quickly building signal was heard on CW calling CQ at about 25wpm ... it was CN8KD in Rabat, Morocco!
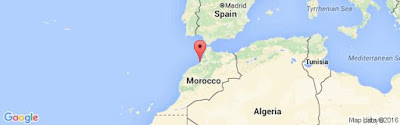 |
| courtesy: https://www.google.ca/maps/ |
I called Mohamed several times as his signal built, but his rapid-fire CQ's continued much to my frustration. As his signal peaked to a solid 569, he sent a '?' and then replied with 'VE6?', probably as shocked as I was. After repeating my call several times, he returned once again but this time with 'VE7NL?'. The next several transmissions from him were the same and as the delicate links between our two stations shifted once again, he was gone as quickly as he'd arrived ... close, but no cigar. This was the first 6m signal that I've ever heard from continental Africa since coming on the band in 1970. I wonder if I will ever hear him again.
With a dead 6m band on Saturday morning, I was able to get back on EME (JT65B mode) for my final day of favorable moonrise windows and had a nice surprise when VE1KG in Nova Scotia answered my first CQ, for initial #81 with my small station ...
... all-in-all, a pretty fun week on the VHF's!
 Having fun on the "Magic Band"
Having fun on the "Magic Band"
Still a relative newcomer to the hobby (only licensed at end of 2013) I had little experience of the 50MHz/6m band and have been mostly met with static whenever I did turn the dial to have a listen but happily that has changed in the last few weeks.
I knew that 6m can be an interesting, unpredictable almost unique band. Being at the lower end of the VHF spectrum it exhibits the usual characteristics of VHF communication, mostly short range line-of-sight contacts since 50MHz is usually well beyond the maximum usable frequency (MUF) for normal 'F-layer' ionospheric propagation utilised by the lower bands. However solar activity and other factors can trigger other types of propagation, in fact the band can support just about every form of propagation possible and is the main reason why it has become known as the "Magic Band"
One interesting form of propagation is sporadic E, or popularly referred to as Es. Small clouds of unusually ionised atmospheric gas form in the lower E-layer of the ionosphere (located at altitudes of 90 to 160 km). These clouds 'bounce' the radio waves allowing long-distance communication at VHF frequencies, sometimes multiple hops are possible giving extreme DX. One advantage of sporadic E over other forms of propagation is that it allows low-power QRP communication. As its name suggests, sporadic E is not a normal occurrence but can happen at almost any time. It does display a seasonal pattern with activity peaking in the summertime most noticeable in mid-to-late June.
I had turned the antenna to the East and have been running WSPR on and off over the last month on 6m with no luck, just the odd spot from the UK. I was in the shack one Saturday evening and was tuning around on 6m and heard some Italian stations calling CQ on SSB. I tried my luck and answered (using 50W) and was amazed to be heard, working a couple of stations in quick succession then suddenly the opening closed mid contact with another station. I was hooked!
Over the past few weeks I have caught a few more openings and have managed to work (in no particular order) Latvia, Croatia, Lithuania, Slovenia, Czech Republic, Slovakia, Serbia, Italy, Germany, Switzerland, Poland, France, Spain, Austria, Canary Islands and Finland - using a combination of voice on SSB and the JT65 digital mode.
Using JT65 has been particularly interesting since it allows me to 'remote operate' from work otherwise I would miss most of the 'Es'. Being able to monitor the waterfall and see the signals gaining and falling in strength during the minute long transmission is particularly fascinating.
Using the PSKReporter website I can see the location of all the stations I could hear and was being heard by. This map shows activity over the couple of hours on the 26 May using just JT65.
I have joined the UK Six Meter Group (UKSMG) to find out more about this "magic band" and their website is full of lots of information and resources along with the magazine Six News for subscribers.
 Having fun on the "Magic Band"
Having fun on the "Magic Band"
Still a relative newcomer to the hobby (only licensed at end of 2013) I had little experience of the 50MHz/6m band and have been mostly met with static whenever I did turn the dial to have a listen but happily that has changed in the last few weeks.
I knew that 6m can be an interesting, unpredictable almost unique band. Being at the lower end of the VHF spectrum it exhibits the usual characteristics of VHF communication, mostly short range line-of-sight contacts since 50MHz is usually well beyond the maximum usable frequency (MUF) for normal 'F-layer' ionospheric propagation utilised by the lower bands. However solar activity and other factors can trigger other types of propagation, in fact the band can support just about every form of propagation possible and is the main reason why it has become known as the "Magic Band"
One interesting form of propagation is sporadic E, or popularly referred to as Es. Small clouds of unusually ionised atmospheric gas form in the lower E-layer of the ionosphere (located at altitudes of 90 to 160 km). These clouds 'bounce' the radio waves allowing long-distance communication at VHF frequencies, sometimes multiple hops are possible giving extreme DX. One advantage of sporadic E over other forms of propagation is that it allows low-power QRP communication. As its name suggests, sporadic E is not a normal occurrence but can happen at almost any time. It does display a seasonal pattern with activity peaking in the summertime most noticeable in mid-to-late June.
I had turned the antenna to the East and have been running WSPR on and off over the last month on 6m with no luck, just the odd spot from the UK. I was in the shack one Saturday evening and was tuning around on 6m and heard some Italian stations calling CQ on SSB. I tried my luck and answered (using 50W) and was amazed to be heard, working a couple of stations in quick succession then suddenly the opening closed mid contact with another station. I was hooked!
Over the past few weeks I have caught a few more openings and have managed to work (in no particular order) Latvia, Croatia, Lithuania, Slovenia, Czech Republic, Slovakia, Serbia, Italy, Germany, Switzerland, Poland, France, Spain, Austria, Canary Islands and Finland - using a combination of voice on SSB and the JT65 digital mode.
Using JT65 has been particularly interesting since it allows me to 'remote operate' from work otherwise I would miss most of the 'Es'. Being able to monitor the waterfall and see the signals gaining and falling in strength during the minute long transmission is particularly fascinating.
Using the PSKReporter website I can see the location of all the stations I could hear and was being heard by. This map shows activity over the couple of hours on the 26 May using just JT65.
I have joined the UK Six Meter Group (UKSMG) to find out more about this "magic band" and their website is full of lots of information and resources along with the magazine Six News for subscribers.
 So just how sporadic is sporadic E (Es)?
So just how sporadic is sporadic E (Es)?
Time and again I have been struck by just how unsporadic Es is. OK, good days are random but there seems to be a pattern that more northerly and Scandinavian stations on 10m and 6m are better later in the day and later in the season. I actually wonder if these more northerly reports really are Es at all. There is every chance I am totally wrong, but I have noticed this over several summers and I question that Es is truly “sporadic”. I’d be interested to hear the views of others on this.
One thing is certain: we still have a great deal to learn about E-layer DX propagation. Es is certainly a fact on many summertime EU QSOs on the higher HF bands and 6m, but I am sure the multi-hop explanation for some very long distance QSOs is not right.
















