Archive for the ‘dx’ Category
 Part 2 of 2: Life-changing Moment and Solar Cycle 25
Part 2 of 2: Life-changing Moment and Solar Cycle 25
From the RAIN HamCast episode #57, 2021-XII-25 (used with permission):
RAIN’s Hap Holly/KC9RP spoke with Tomas recently about Solar Cycle 25. This is the second and final excerpt from their discussion.
From the introduction to The RAIN HamCast, Episode #57:
In this episode, we continue our discussion with Tomas Hood/NW7US, the author of many writings about space weather and effects of solar activity the past 20-plus years.
(Part 1 of 2 can be found here: Episode #56, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HnuSOXhFELQ)
Tomas has been a short wave enthusiast since 1973, a ham operator since 1990, and is a United States Army Signal Corps veteran today. He launched the first civilian space weather propagation website, HFRadio.org, in the mid 90’s; HFradio later spawned SunSpotWatch.com; at press time Sunspotwatch.com is being revamped for the new Solar Cycle 25.
Tomas has contributed to the Space Weather Propagation column in CQ magazine for over 20 years, and for The Spectrum Monitor magazine since 2014. A product of the Pacific northwest, Tomas resides now in Fayetteville, Ohio.
RAIN’s Hap Holly/KC9RP spoke with Tomas recently about Solar Cycle 25. This is the second and final excerpt from their discussion.
Here is the second part of the two-part interview:
If you missed part one of this conversation, you’ll find it as RAIN Hamcast #56 both on therainreport.com and on the RAIN Hamcast page on YouTube, as well as here: Episode #56, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HnuSOXhFELQ.
RAIN Hamcast #58 will post January 8, 2022. Hap Holly/KC9RP edits and produces this biweekly ham radio podcast. It is copyright 1985-2021 , RAIN, all rights reserved. RAIN programming is made available under a Creative Commons license ; you are encouraged to download, share, post and transmit the RAIN Hamcast in its entirety via Amateur Radio. Your support and feedback are welcome on therainreport.com. Thanks for YouTube Technical Assistance from Tom Shimizu/N9JDI. I’m Will Rogers/K5WLR bidding you very 73 and 44 from the Radio Amateur Information Network.

KEEP ON HAMMING!
Footnote: Yes, NW7US misspoke about the time it takes sunlight to travel from the Sun to the Earth. He meant that it takes sunlight and radio waves just over 8 minutes to make that trip…
 Solar Cycle 25, and a Life-Changing Event (Part 1 of 2)
Solar Cycle 25, and a Life-Changing Event (Part 1 of 2)
From the RAIN HamCast episode #56, 2021-XII-11 (used with permission):
When you were knee high to a grasshopper, did you undergo a game-changing experience that shaped your future career?
Here is text from the introduction:
Tomas Hood/NW7US did. Tomas has been a shortwave enthusiast since 1973. He was first licensed as a ham in 1990 at age 25.
In the mid 1990s Tomas launched the first civilian space weather propagation website, HFRadio.org, which later spawned SunSpotWatch.com. His website, NW7US has been up and running since June, 1999. Tomas has contributed to the Space Weather Propagation column in CQ magazine for over 20 years, and for The Spectrum Monitor magazine since 2014.
A product of the Pacific northwest, Tomas resides today in Fayetteville, OH. RAIN’s Hap Holly/KC9RP spoke with Tomas recently about Solar Cycle 25 and the game-changing afternoon Tomas experienced in 1973 at age 8 ( Read more about this, at his amateur radio and space weather blog: https://blog.NW7US.us/ ).
Here is the first part of the two-part interview:
Mentioned in the interview is Skylab:
From Wikipedia’s article on Skylab: Skylab was the first United States space station, launched by NASA, occupied for about 24 weeks between May 1973 and February 1974. It was operated by three separate three-astronaut crews: Skylab 2, Skylab 3, and Skylab 4. Major operations included an orbital workshop, a solar observatory, Earth observation, and hundreds of experiments.

Tomas was drawn into space weather as a life-long passion, by inspiration from Skylab, and from the hourly propagation bulletin from the radio station WWV.
WATCH FOR THE NEXT EPISODE, PART TWO
This video is only part one. The RAIN HamCast will conclude Hap’s conversation with Tomas in RAIN HamCast #57, scheduled for posting Christmas Day.

Hap Holly, of the infamous RAIN Report (RAIN = Radio Amateur Information Network), is now producing The RAIN HamCast. The results are both on https://therainreport.com and on the RAIN HamCast YouTube channel, https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCUbNkaUvX_lt5IiDkS9aS4g
KEEP ON HAMMING!
The RAIN Hamcast is produced and edited by Hap Holly/KC9RP; this biweekly podcast is copyright 1985-2021 RAIN, All rights reserved. RAIN programming is formatted for Amateur Radio transmission and is made available under a Creative Commons license; downloading, sharing, posting and transmission of this ham radio program via Amateur Radio in its entirety are encouraged. Your support and feedback are welcome on https://therainreport.com. Thanks for YouTube Technical Assistance from Tom Shimizu/N9JDI.
 2nd X-class X-ray Flare in New Solar Cycle 25 – October 28, 2021
2nd X-class X-ray Flare in New Solar Cycle 25 – October 28, 2021
This imagery captured by NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO; link) covers a busy period of activity in October, during which we witnessed an X1.0-class X-ray flare.
From late afternoon October 25 through mid-morning October 26, an active region on the left limb of the Sun flickered with a series of small flares and petal-like eruptions of solar material.
Meanwhile, the Sun was sporting more active regions at its lower center, directly facing Earth. On October 28, the biggest of these released a significant flare, which peaked at 15:35, 28 Oct 2021 UTC.
This X1.0 X-ray flare that erupted from Active Region 12887 (we typically drop the left-most digit when referring to an active region, so this is AR2887) is the second X-class flare of Solar Cycle 25, as of the time this video goes live.
The first X-class flare occurred on 3 July 2021 and measured X1.59. It, too, caused an HF radio blackout. These blackouts will occur more often as the cycle activity increases, because the higher sunspot activity leads to many more flares, and thus cause the geomagnetic storms as the typical CME is erupted out into space, possibly colliding with Earth’s magnetosphere.
Solar flares are powerful bursts of radiation. Harmful radiation from a flare cannot pass through Earth’s atmosphere to physically affect humans on the ground. When intense enough, they can disturb the atmosphere in the layer where GPS and communications signals travel. Some of these disturbances to communications are called radio blackouts. They cause the lower layers of the ionosphere to become more ionized, which results in the absorption of shortwave radio frequency signals.
This flare on October 28 was classified as X1.0 in intensity. X-class denotes the most intense flares, while the number provides more information about its strength. An X2 is twice as intense as an X1, an X3 is three times as intense, and so on. Flares that are classified X10 or stronger are considered unusually intense.
This was the second X-class flare of Solar Cycle 25, which began in December 2019. A new solar cycle comes roughly every 11 years. Over the course of each cycle, the Sun transitions from relatively calm to active and stormy, and then quiet again; at its peak, known as solar maximum, the Sun’s magnetic poles flip.
Two other eruptions blew off the Sun from this active region: an eruption of solar material called a coronal mass ejection and an invisible swarm of solar energetic particles. These are high-energy charged particles accelerated by solar eruptions.
Credit: NASA/GSFC/SDO
Thanks for liking and sharing!
73 de NW7US dit dit
 Part time radio weekend.
Part time radio weekend.
In Canada and the U.S. this is a long weekend (Labour Day Weekend) with Monday being a holiday. I was able to spend a little time on the radio in the late afternoon a few days of the long weekend. I was able to spend a few hours on both Saturday and Sunday. For the most part I spent my time on 20m CW and both days the bands seemed to not be too busy. As I spent some time on the radio I found the bands were not that quiet. It was deep QSB that was working its magic to drop an S9 signal just at or below the noise floor.
Having a radio with a waterfall is a great advantage and my Icom 7610's waterfall came in very handy showing me a signal before they would fade away to nothingness. I heard 4X6FR from Israel calling CQ and I was surprised he did not have a pile up. I gave him a few calls but he answered other stations. Not a problem I would just wait it out. This is where the QSB kicked in and within a very short time I found only static and no 4X6FR! The 7610 has 2 independent receivers which is a great advantage. In this case with my headphones I listened for a reappearance of 4X6FR in my left ear or VFO B. The right ear VFO A was scanning other signals that appeared on the waterfall. Needless to say, the station from Israel never again showed up on the waterfall, but he was still out there as he was being spotted by U.S. stations on DX Summit.
As time went on the best way to describe what I saw on the waterfall was "now you see them and now you don't" When I did tune on some DX and made contact it was touch and go to make a fast and simple RST exchange and if I felt lucky I added my name and location. I was pleased with my radio time and made contact with 4O4T in Montenegro, R5AF, SP6AEG, LZ305AI, IK5OPR and finally TZ4AM from Mali which was a new one for me. I saw him being spotted on 17meters and I decided to venture there as 20m was getting a bit slow.
The spot indicated "up 1" which meant there was a pile up and he was operating split. I skipped over to 17 meters and then landing myself on his calling frequency just to make sure I could hear him before I got too excited. There he was at S6 and I knew I had to move fast as the deep QSB had robbed me a few times from catching nice DX. I set my radio to split and dual watch which allows me to hear the DX and those who are calling him. BUT strange thing no one was calling him and my waterfall was void of signals. It could be the QSB playing games with me. So when I heard him call CQ I put my call out and he came back to me on my first call. TZ4AM was in the log and I was happy. Very shortly after the contact the deep QSB took the signal from the waterfall.
It's Monday today and I was busy getting some household chores done throughout the day. Maybe this evening I will be back on the radio and see how 40m treats me.
 Interested in Amateur Radio Digital Mode FT8 Operations?
Interested in Amateur Radio Digital Mode FT8 Operations?
A VISUAL + AUDIO AIR CHECK OF DIGITAL MODE FT8 QSOs, ON THE 30-METER BAND
Here is a video capture of the reception and transmission of many digital FT8-mode amateur radio high-frequency (HF; Shortwave) communication signals. This video is a front-seat view of the software operation performed at the radio room of amateur radio operator, NW7US, Tomas Hood.
The software packages demonstrated are installed and operational on a modern personal computer. The computer is connected to an Icom IC-7610 radio transceiver, controlled by the software. While there is no narration in the video, the video provides an opportunity for you to see first-hand how typical FT8 operations are performed. The signals can be heard.
The frequency used for the FT8 communication in this video is on or about 10.136 MHz, in the 30-Meter shortwave amateur radio allocation (or, band). As can be seen, the 30-Meter band was active at this time of day (0720 UTC, onward–local nighttime).
In this video you see (and hear) NW7US make two-way contacts, or QSOs, with stations from around the country and the world.
There are amateur radio operators within the amateur radio community who regard the FT8 digital mode (FT8 stands for “Franke-Taylor design, 8-FSK modulation“, and refers to the mode created by Joe Taylor, K1JT and Steve Franke, K9AN) as robotic (automatic, automated, and unattended) computer-to-computer communications, and not ‘true’ human communications–thus negating the spirit of ham radio. In other words, FT8, in their opinion, is not real amateur radio. While they pontificate about supposed automated computer communications, many of those holding this position have not installed and configured the software, nor tried communicating with the FT8 digital mode. They have perhaps formed their anti-FT8 opinion in a vacuum of knowledge. (This writer has other issues with FT8, but not on this point–see below)
As you watch the video linked in this article, consider these concepts:
+ A QSO is defined (as per common knowledge–see below) as the exchange of at least the minimum information needed as set by the requirements of a particular award, or, as is defined by law–for instance, a QSO would have at least an exchange of the legal call sign assigned to the radio station and/or control operator, the location of the station making the transmission, and a signal report of some kind about the signal received from the other transmitter at the other end of the QSO.
+ Just how much human involvement is required to make a full FT8 QSO? Does WSJT-X software run all by itself, with no human control? Is WSJT-X a robot, in the sense that it picks a frequency, then initiates or answers a CQ call automatically, or is it just powerful digital-mode software that still requires human control?
The video was captured from the screen of the PC running the following software packages interacting together as a system:
+ WSJT-X: The primary software featuring the digital mode, FT8. (See below for some background on WSJT-X software.)
+ JTAlert: Provides several audio and visual alert types based on decoded Callsigns within WSJT-X.
+ Log4OM, Version 2: A full-featured logging program, which integrates well with WSJT-X and JTAlert.
+ Win4IcomSuite: A full-featured radio controlling program which can remote control rigs, and provide control through virtual communication port-sharing.
+ Com0Com: The Null-modem emulator allows you to create an unlimited number of virtual COM port pairs and use any pair to connect one COM port based application to another. Each COM port pair provides two COM ports. The output to one port is the input from other port and vice versa.
As mentioned, above, the radio used for the communication of FT8 at the station, NW7US, is an Icom IC-7610 transceiver. The antenna is an off-center fed dipole that is over 200 feet in total length (end-to-end measurement).
Some Notes:
About WSJT-X
WSJT-X is a computer program used for weak-signal radio communication between amateur radio operators, or used by Shortwave Radio Listeners (SWLers; SWL) interested in monitoring the FT8 digital communications between amateur radio operators. The program was initially written by Joe Taylor, K1JT with Steve Franke, K9AN, but is now open source and is developed by a small team. The digital signal processing techniques in WSJT-X make it substantially easier for amateur radio operators to employ esoteric propagation modes, such as high-speed meteor scatter and moonbounce.
WSJT-X implements communication protocols or “modes” called FST4, FST4W, FT4, FT8, JT4, JT9, JT65, Q65, MSK144, and WSPR, as well as one called Echo for detecting and measuring your own radio signals reflected from the Moon. These modes were all designed for making reliable, confirmed QSOs under extreme weak-signal conditions. JT4, JT9, and JT65 use nearly identical message structure and source encoding (the efficient compression of standard messages used for minimal QSOs). They use timed 60-second Transmit/Rreceive (T/R) sequences synchronized with UTC (Universal Time, Coordinated). JT4 and JT65 were designed for Earth-Moon-Earth communications (EME, or, moonbounce) on the Very-High Frequency (VHF), Ultra-High Frequency (UHF) and microwave bands. JT9 is optimized for the Medium-Frequency (MF) and High-Frequency (HF) bands. It is about 2 dB more sensitive than JT65 while using less than 10% of the bandwidth. Q65 offers submodes with a wide range of T/R sequence lengths and tone spacings.FT4 and FT8 are operationally similar but use T/R cycles only 7.5 and 15 seconds long, respectively. MSK144 is designed for Meteor Scatter on the VHF bands. These modes offer enhanced message formats with support for nonstandard call signs and some popular contests. (The MSK in MSK144 stands for, Multiple Frequency Shift Keying.)
FST4 and FST4W are designed particularly for the Low-Frequency (LF) and MF bands. On these bands, their fundamental sensitivities are better than other WSJT-X modes with the same sequence lengths, approaching the theoretical limits for their rates of information throughput. FST4 is optimized for two-way QSOs, while FST4W is for quasi-beacon transmissions of WSPR-style messages. FST4 and FST4W do not require the strict, independent time synchronization and phase locking of modes like EbNaut.
As described more fully on its own page, WSPR mode implements a protocol designed for probing potential propagation paths with low-power transmissions. WSPR is fully implemented within WSJT-X, including programmable band-hopping.
What is a QSO?
Under the title, CONTACTS, at the Sierra Foothills Amateur Radio Club’s 2014 Technician Class webpage, https://www.hsdivers.com/Ham/Mod15.html, they teach,
An amateur radio contact (called a QSO), is an exchange of info between two amateur radio stations. The exchange usually consists of an initial call (CQ = call to all stations). Then, a response from another amateur radio operator, and usually at least a signal report.
Contacts can be limited to just a minimal exchange of call signs & signal reports generally between amateurs previously unknown to each other. Very short contacts are usually done only during contests while longer, extended ‘rag chews’ may be between newly met friends with some common interest or someone you have known for a long time.
Wikipedia has an entry for QSO, too.
My Issue With FT8 and WSJT-X
I have written in the past, on this website, about an issue that came about during the course of the development of the WSJT-X software package. The development team decided to widen the slice of ‘default’ (pre-programmed) frequencies on which to operate FT8. The issue was how the choice of new frequencies was made, and what choices were implemented in an upcoming software release. Read more about all of this, in these three articles:
+ Land (er, FREQUENCY) Grab (Part 1)
+ One Aspect of Amateur Radio: Good Will Ambassadors to the World
+ In Response — Can’t We All Just Get Along?
Has this issue been resolved? For now, yes. There appears to be more coordination between interested groups, and the proposed new frequencies were removed from the software defaults in WSJT-X. At least, up to this point, at the time of publishing this article.
..
 New Antenna: The Following Footprints Are of My CW Signals (2021-March-14 @ 04:00 to 04:20 UTC).
New Antenna: The Following Footprints Are of My CW Signals (2021-March-14 @ 04:00 to 04:20 UTC).
The following footprints are of my CW signals on 2021-March-14 at about 04:00 to 04:20 UTC.
Click on this image to see a larger version of this image:
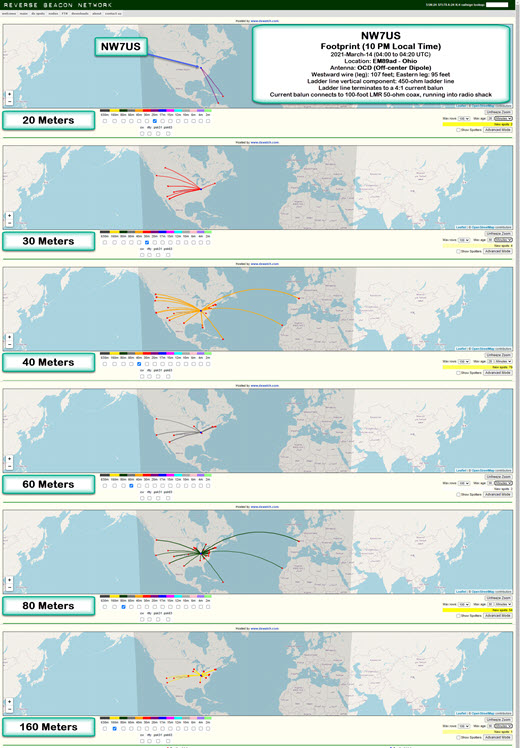
Location: EM89ad – Ohio
Antenna: OCD (Off-center Dipole)
Description of Antenna:
This is an off-center dipole, with the two legs running East-East-South (approximately 125 degrees of North), and West-West-North (about 306 degrees on the compass). The westward wire (leg) is approximately 107 feet in length, while the eastward leg is about 95 feet in length.
These legs (an off-center-fed dipole) is directly connected to about 90 feet of 450-ohm ladder line, which is hanging directly below, vertically, the feed point. The feed point is 50 feet above the ground.
The ladder line terminates (at the 12-feet-above-ground point) to a 4:1 current balun. This current balun then connects to a 100-foot LMR 50-ohm coax, which is running into the radio shack. It is connected via an antenna switch to my Icom IC-7610 transceiver. I am transmitting a 100-watt CW signal using an Icom IC-7610, in the following format:
TEST TEST TEST DE NW7US NW7US NW7US
The Reverse Beacon Network reports any spotting of this test transmission. The beta mapping interface, at http://beta.reversebeacon.net/main.php, then maps the resulting spots. To learn more about the RBN, visit http://beta.reversebeacon.net/index.php, or, http://reversebeacon.net/index.php.
I show the 20-, 30-, 40-, 60-, 80-, and 160-Meter band footprints.
I’ve been capturing these CW transmission spots, at different times of the day, today. I’ll get data from several days, at regular intervals, and create a overview of how the antenna appears to be working during this month and under these propagation conditions.
73 de NW7US dit dit
..












