Archive for the ‘dx’ Category
 Notes from the shack
Notes from the shack
 Over winter break I have been putting in a lot of time behind the radio. Here’s the wrap up:
Over winter break I have been putting in a lot of time behind the radio. Here’s the wrap up:
First – more DX. In general, this is a good time of year to catch hams behind their rigs. Some contacts that I am particularly proud of:
4U1WB, The World Bank in Washington D.C.
ZD7DL, St Helena Island
WH6S, Kauai
C5YK, The Gambia
9H5BZ, Malta
MI5AFK, Northern Ireland
FG5GP, the island of Guadeloupe
ZS6TVB, South Africa
EA8DAZ, Canary Islands
VP2ETE, Anguilla
Second – working a lot of DX. There is the 90th anniversary of the International Amateur Radio Union (IARU) special event activations. Plenty of good DX participating in this and working multiple bands.
Cuba
Bermuda
Finland
Germany
Aruba
Venezuela
Jamaica
Ireland
Italy
Slovenia
Brazil
Third – working Santa (aka AA4EE) on Christmas Eve. The girls really enjoyed telling Santa what they wanted. Thank you Santa!
Four – joining the OMISS and the 3905 Century Club nets. I am not sure if I fully understand these nets. I get the convenience in pursuing Worked All States awards. That makes sense. However each club also has an additional bevy of other types of awards. The actual contacts during the nets seem a bit unfulfilling. But I may not yet fully understand these nets. I need to thoroughly read all the literature.
Five – Log of the World: I have uploaded the vast majority of my logs. I mentioned before about uploading my YI9MI logs. I also went back and uploaded my log from KD7PJQ back in Virginia. The logs from Korea (HL2/AD7MI and HL9MI) are now uploaded. All my logs using AD7MI have been uploaded.
 An interesting challenge
An interesting challenge
http://ny4g.blogspot.com/2015/12/qrp-dxcc-challenge.html
He calls it "QRP Wars - The Morse Awakens".
Cute.
Now the question is - can it be done?
My answer is, "Yes, I think it can." Even with the worsening solar conditions. But (and there's alway's a "but") I think this competition favors those who are retired and can send mondo amounts of time on the radio. It also favors those of us on the East coast, who are closer to Europe and the Caribbean. And with the ARRL DX Contest which is held in February, if you really put your mind to it, it should be possible to work QRP DXCC within 100 days.
Am I going to put my money where my mouth is?
Not sure at this point. I just might try it for fun and just may keep a "diary" of the effort here on the blog - just for the halibut. Let me cogitate on it for a while. I have a couple of days left until 2016 rolls around.
72 de Larry W2LJ
QRP - When you care to send the very least!
 Get Ready: Month-long Special Event for SKCC, the 2016 K3Y Celebration
Get Ready: Month-long Special Event for SKCC, the 2016 K3Y Celebration
Are you ready for the annual, month-long special event by the Straight Key Century Club (SKCC)? The SKCC Group membership is free, and celebrates the longest tradition of amateur radio: Morse code. But, not just any Morse code. The manual creation of Morse code by “straight” keys means no electronic origin, only mechanical. This is a month-long event, during January 2016, modelled after the ARRL Straight Key Night.
Here’s a video that I made showing my activity as the control operator of the special event station, K3Y/0, during one of the many shifts during January (2015). K3Y is the special event callsign of the Straight Key Century Club (SKCC). The special event operates each January. I’ll be doing this again, this coming month, January of 2016.
K3Y, the Straight Key Century Club’s annual January celebration, commemorates the club’s founding in 2006 following the American Radio Relay League’s Straight Key Night. A small group of participants wanted to extend the fun of SKN throughout the year. The SKCC is the result.
For the first three years, the club’s founders used K1Y, K2A, and K3Y as the celebration’s special-event calls. But someone cleverly noticed that a 3 is nothing more than a backwards, curvaceous E. This “KEY” event has operated under the K3Y call ever since.
The on-air party is open to members and non-members alike. It runs from 0000 UTC Jan. 2 through 2359 UTC Jan. 31. It’s a great time to introduce others to the joys of hand-crafted Morse code using straight keys, bugs, and side swipers.
This year, January 2016, we’ll be fielding K3Y operators in each of the 10 US call areas, plus KH6, KL7 and KP4, along with specially scheduled stations in each of six IARU continental regions. Your QSOs with event operators in all these 19 areas will be tabulated in the Statistics section and can be confirmed with a K3Y QSL card and Sweep Certificate.
+ The SKCC website is at http://skccgroup.com
+ The K3Y special event page is http://www.skccgroup.com/k3y/
73 de NW7US
dit dit
 Tomorrow is always another day
Tomorrow is always another day
I started my lunchtime QRP session fully intending to work the N3AQC QRP-pedition to the USS Requin which is docked by the Carnegie Science Center in Pittsburgh. John K3WWP and Mike KC2EGL were there today, and I figured that maybe, just maybe, I might be able to hear them on 40 Meters. So I set up the Buddistick for that band - magmount base, all four 11 inch arms, untapped coil, extra long whip. I was able to get the SWR down to about 1.5:1 and I heard plenty of signals, but no N3AQC. They started at 10:00 AM, and by the time I was able to get to the parking lot, it was 1:30 PM, so I don't know if they were on lunch break also, or perhaps they had just called it a day by then, or perhaps they were on 20 and 30 Meters. But tuning around for about 15 minutes and not hearing N3AQC, I decided to switch over to the higher bands, as lunch time is only an hour.
So I took two of the 11" arms off, put the coil tap in its accustomed position and put the Buddistick back on the roof. Tuning around, at 14.018 MHz, I heard them - PZ5W - Suriname. The same station from yesterday, and they were even louder than they were on 15 Meters. So without even thinking, I dialed in a 1kHz up split and gave a call ... and was heard. I sent my info and completed the exchange and then looked down at the KX3.
In my haste, I hadn't touched up the SWR with the autouner. My SWR was 1.7:1 and the KX3's power had folded back to 3 Watts. So what I couldn't accomplish with 5 Watts yesterday, got done with 3 Watts today. That felt nice - really, really nice.
Looking at my watch, I saw I had about 15 minutes left before I had to break down and go back into the building, so I prowled around the band some more for a few minutes. Lo and behold, T2TT - Tuvalu coming in loud and clear! Argh! Ten minutes was not enough to even consider it a decent try, but I did - and failed.
But ...... tomorrow is always another day.
72 de Larry W2LJ
QRP - When you care to send the very least!
 DX seems to operate in the fast lane
DX seems to operate in the fast lane
DX for new CW operators
How to copy those high speed ops?
 |
| EA8TL's Hexbeam in the Canary Islands |
Anyway I was happy to get the response. I know (or surmise) that my 80m Windom has some fairly pronounced gain nodes in different directions on the higher bands but I didn't know which directions they pointed. I guess one of the nodes points toward Africa (yaaay!)
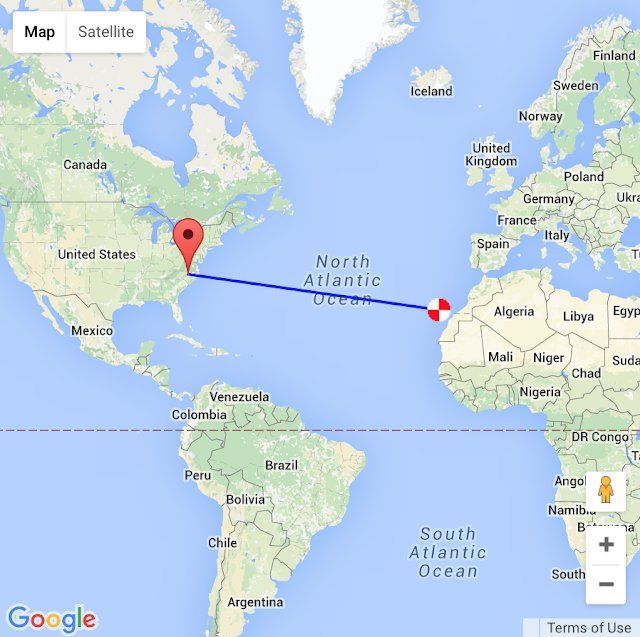 |
| Path from N4PBQ to EA8TL in the Canary Islands |
Do DX operators just not want to bother with newbies such as myself? I wonder. I'd appreciate suggestions in the comments section.That's all for now
So lower your power and raise your expectations
73/72
Richard N4PBQ
 What is the big deal with amateur radio? What is it that you hear? (Part 1)
What is the big deal with amateur radio? What is it that you hear? (Part 1)

Shortwave radio has been a source for great sci-fi plots, spy intrigue novels, movies, and so on, since radio first became a “thing.” But, what is the big deal, really? What is it that amateur radio operators listen to?
In this video, I share some of the types of signals one might hear on the high frequencies (also known as shortwave or HF bands). This is the first video in an on-going series introducing amateur radio to the interested hobbyist, prepper, and informed citizen.
I often am asked by preppers, makers, and other hobbyists, who’ve not yet been introduced to the world of amateur radio and shortwave radio: “Just what do you amateur radio operators hear, on the amateur radio shortwave bands?”
To begin answering that question, I’ve taken a few moments on video, to share from my perspective, a bit about this shortwave radio thing:
Link to video: https://youtu.be/pIVesUzNP2U — please share with your non-ham friends.
From my shortwave website:
Shortwave Radio Listening — listen to the World on a radio, wherever you might be. Shortwave Radio is similar to the local AM Broadcast Band on Mediumwave (MW) that you can hear on a regular “AM Radio” receiver, except that shortwave signals travel globally, depending on the time of day, time of year, and space weather conditions.
The International Shortwave Broadcasters transmit their signals in various bands of shortwave radio spectrum, found in the 2.3 MHz to 30.0 MHz range. You might think that you need expensive equipment to receive these international broadcasts, but you don’t! Unlike new Satellite services, Shortwave Radio (which has been around since the beginning of the radio era) can work anywhere with very affordable radio equipment. All that you need to hear these signals from around the World is a radio which can receive frequencies in the shortwave bands. Such radios can be very affordable. Of course, you get what you pay for; if you find that this hobby sparks your interest, you might consider more advanced radio equipment. But you would be surprised by how much you can hear with entry-level shortwave receivers. (You’ll see some of these radios on this page).
You do not need a special antenna, though the better the antenna used, the better you can hear weaker stations. You can use the telescopic antenna found on many of the portable shortwave radios now available. However, for reception of more exotic international broadcasts, you should attach a length of wire to your radio’s antenna or antenna jack.
 The Gray Line Report
The Gray Line Report
Ham club newsletters exist in abundance. Most to inform members about upcoming events or to celebrate recently concluded activities with words and pictures. But there are those that serve a much larger audience — with timely advice and stories that cover the broader spectrum of amateur radio.
One of my favorites is The Gray Line Report — a quarterly publication of the Twin City DX Association.
The September edition is another good one. I’m reading ‘Adding an Amplifier to a Low Power Contest Station’ by Al Dewey, K0AD.
An there’s plenty more where that came from. Don’t miss it.
Tagged: dx, newsletter, tcdxa
![]()













